What is the Port Forwarding Checker Tool?
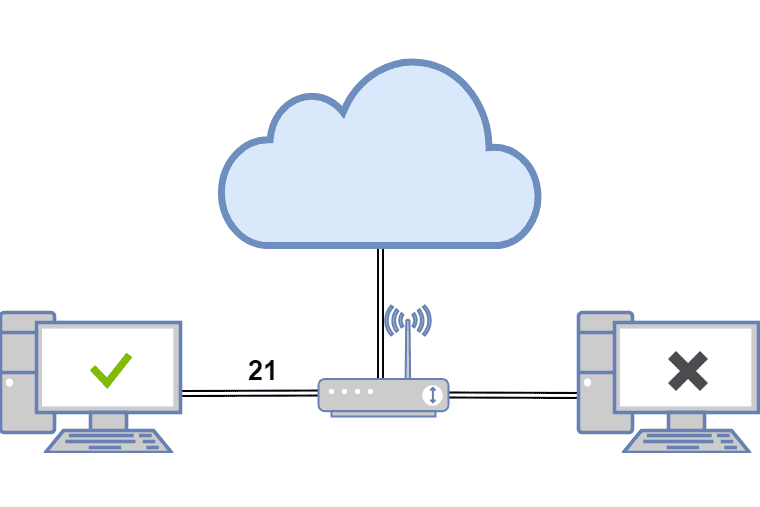
 Port Checker tool is a simple and free online tool for checking open ports on your computer/device, often useful in testing port forwarding settings on a router. If you’re facing connection issues with a program (email, IM client, etc), then it may be possible that the port required by the application is getting blocked by your router’s firewall or your ISP. In some cases, this tool might help you in diagnosing any problem with the firewall setup.
Port Checker tool is a simple and free online tool for checking open ports on your computer/device, often useful in testing port forwarding settings on a router. If you’re facing connection issues with a program (email, IM client, etc), then it may be possible that the port required by the application is getting blocked by your router’s firewall or your ISP. In some cases, this tool might help you in diagnosing any problem with the firewall setup.
You could also find this useful for security purposes, in case you’re not sure whether a particular port is open or closed. For hosting and playing games like Minecraft, use this checker to make sure the server port(25565) is configured properly for the Port Forwarding Checker Tool, and then only your friends will be able to connect to your server.
Most Used Ports
Port numbers from 1 to 65535, out of which well-known ports are predefined as convention by IANA.
0-1023 – Well-known ports (HTTP, SMTP, DHCP, FTP, etc.)
1024-49151 – Reserved Ports
49152-65535 – Dynamic/Private Ports
Well-known ports
20/21 – FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
22 – SSH (Secure Shell)
23 – Telnet, a Remote Login Service
25 – SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
53 – DNS (Domain Name System)
80 – HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
110 – POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3)
115 – SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol)
123 – NTP (Network Time Protocol)
143 – IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol)
161 – SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol
194 – IRC (Internet Relay Chat)
443 – SSL / HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
445 – SMB
465 – SMTPS (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol over SSL)
554 – RTSP (Real Time Stream Control Protocol)
873 – RSYNC (RSYNC File Transfer Services)
993 – IMAPS (Internet Message Access Protocol over SSL)
3389 – RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)
5631 – PC Anywhere
3306 – MySQL
5432 – PostgreSQL
5900 – VNC
6379 – Redis
8333 – Bitcoin
11211 – Memcached
25565- Minecraft
If you’re looking for more ports or the full list of port numbers, check out this Wikipedia page. I’ve listed all the common ports above; feel free to enter any custom port number to check. By default, this site is taking your device’s IP address as the target IP address (the device through which you’re visiting this web page), but you can change the IP addresses – remote clients and servers. But, please don’t misuse this option, otherwise, I would have to restrict the IP address to source again (as I had done earlier). Please keep in mind that if you’re using a VPN or proxy servers, then it may not be able to get your device’s IP correctly.